
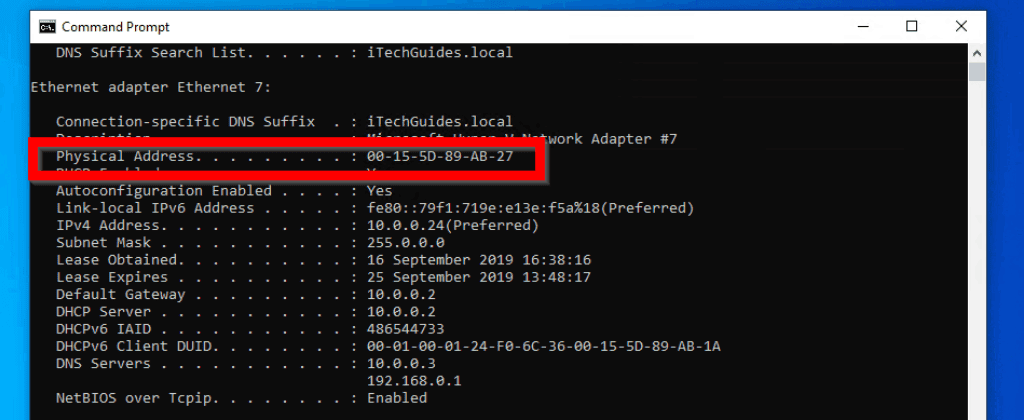
In this communication, the server and your device must know to whom it must send a message, and this is where IP addresses come in handy. If the server responds, the information you requested is sent back to your device. The request is then routed to the device or server with this IP address. The link/ether field associated with your ethernet interface is your MAC address.Every device on a network has a unique address called its IP address, and this helps identify the device and enables other devices to communicate with it.įor example, when you type a URL in your browser, such as, what essentially happens is that your device sends the URL to a Domain Naming Server that translates this URL to an IP address. The "Ethernet Address" field for the ethernet hardware port is your MAC address. Type " networksetup -listallhardwareports". Click on the Advanced button on the right, and then the Hardware tab.Make sure that the ethernet interfaces is selected on the left side.Go to the Apple menu > System Preferences > Network (under "Internet and Wireless").Make sure you're looking at your ethernet interface and not your wireless interface. The Physical Address value for your ethernet card is your MAC address. When the command window appears, type ipconfig /all. For PCs running Windows 8 and later, launch the "Command" program by searching for it in your applications list. Finding the Ethernet MAC Address Microsoft Windowsįor PCs running Windows 7 and earlier, Go to Start Menu > Programs > Accessories > DOS Command Prompt.
Both wired and wireless network interfaces have these addresses. It is a 12 digit hexadecimal number usually delimted by colons, e.g.
Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
